Org Roles
Introduction
This REST API provides endpoints to manage and query various role-related data structures used in a dynamic role-assignment system. The system is designed to handle subject-role relationships, group constraints, role applications, and assignment policies through both static and dynamic configurations.
The APIs enable the following operations:
- Assigning or removing roles from subjects
- Managing metadata about role types (such as assignment behavior, evaluation DSLs, auction workflows, etc.)
- Managing group constraints associated with specific groups
- Tracking applications made for roles
- Querying subject-role and role-group associations
The system supports dynamic, multi-subject, single-subject, and fixed role types. Using this API, you can configure how roles are evaluated, assigned, and removed through DSLs (Domain-Specific Logic workflows), and track all interactions and configurations in MongoDB collections.
These endpoints are grouped based on the associated MongoDB collections, and follow common CRUD patterns. Some endpoints are restricted to read-only access to ensure consistency and integrity of core mappings.
Architecture
The Org Roles Management System is a multi-path, extensible architecture designed to manage the full lifecycle of role assignments in federated, policy-controlled organizational environments. It supports declarative role specification, constraint-aware execution, dynamic subject matching, auction-based selection, and subject-driven application flows.
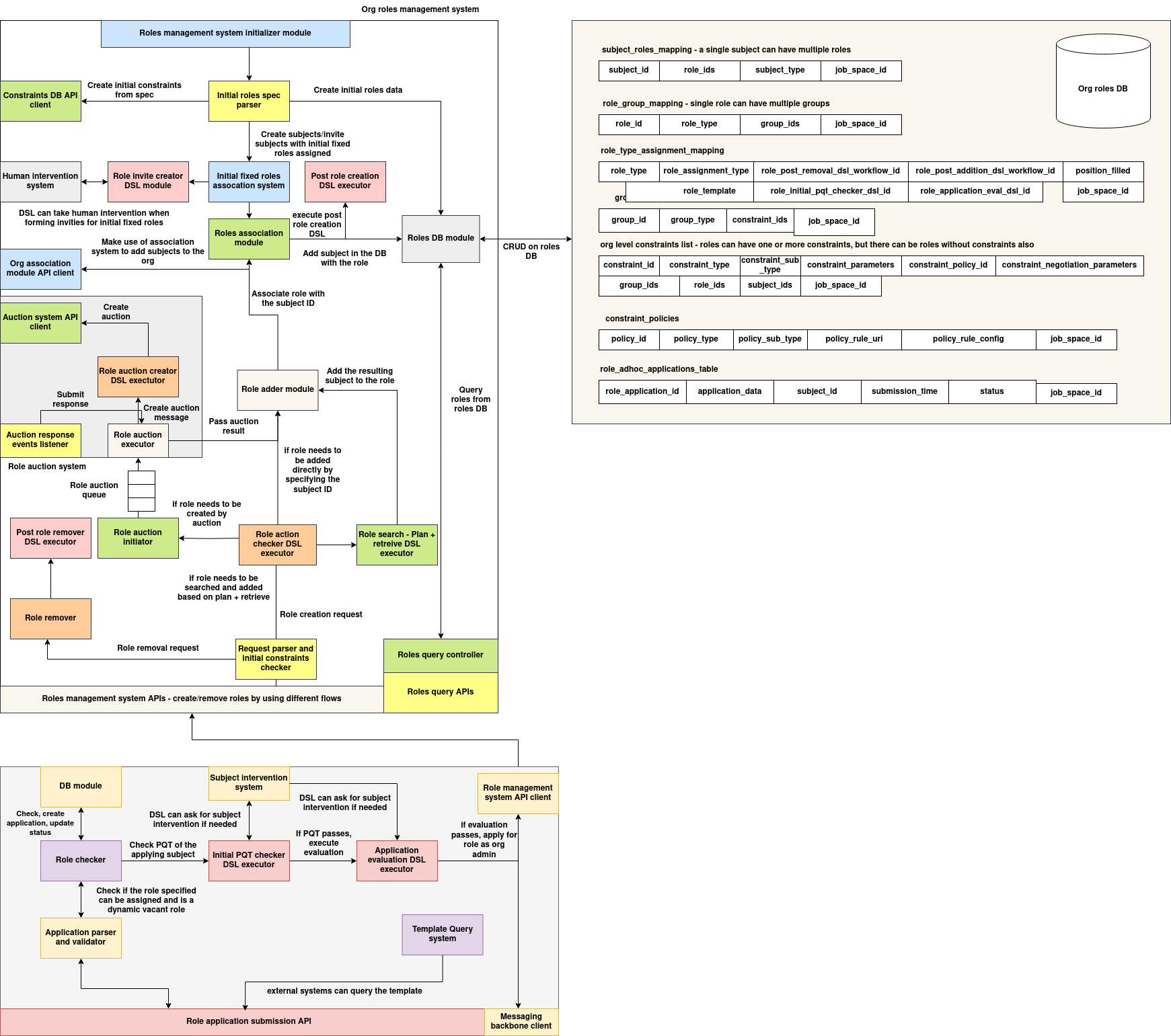
The architecture is modular and built around two primary execution paths:
- Role Lifecycle Management – Creation, assignment, and removal of roles using system-initiated flows such as fixed definitions, DSL plans, and auctions.
- Role Application Submission – Subject-initiated workflows that enable dynamic application, evaluation, and acceptance based on eligibility criteria.
These flows are supported through declarative DSL modules, multiple backend clients, and a shared role datastore. Each action is validated through constraints, policies, and runtime conditions before committing to persistent mappings.
Core Architectural Concepts
1. Initialization and Fixed Role Assignment
The system starts with a Roles Management Initializer that parses initial DSL specifications and populates fixed role assignments using the Initial Roles Spec Parser and Initial Fixed Roles Association System. It creates users with predetermined roles and persists them via the Roles Association Module into the Roles DB Module. Optional post-creation logic is handled via the Post Role Creation DSL Executor.
2. Dynamic Role Creation and Execution
Dynamic roles follow three distinct creation paths:
-
Auction-Based: The Role Auction Initiator invokes the Role Auction Creator DSL, which triggers asynchronous auctions through the Auction System API. Results are consumed by a listener and forwarded to the Role Adder Module.
-
Plan and Retrieve: For intelligent subject discovery, the Role Action Checker DSL Executor delegates to the Role Search - Plan + Retrieve DSL Executor, which dynamically finds eligible candidates based on constraints.
-
Direct Addition: If a subject is pre-specified, the system skips search/auction and directly adds the role using the Role Adder Module.
Each creation path validates business logic via DSLs and submits the result to the Roles DB.
3. Role Removal Path
Role removals are initiated through an external Role Remover call, which triggers the Post Role Remover DSL Executor to validate if the role can be safely disassociated. Validated removals are committed by updating mappings in the DB.
4. Role Application Flow (Subject-Initiated)
Subjects can apply for roles through the Role Application Submission API, which is routed to an asynchronous evaluator pipeline:
- Parser & Validator checks schema and request structure.
- Role Checker ensures the target role is dynamic and unfilled.
- Initial PQT DSL Executor validates preliminary eligibility.
- If needed, the Subject Intervention System handles approvals or escalations.
- Application Evaluation DSL Executor runs the core role evaluation logic.
- Upon success, the Role Management System API Client adds the subject to the role and updates the DB.
This pipeline ensures eligibility enforcement, auditability, and human-in-the-loop flexibility.
5. Extensibility via DSLs and Auctions
The architecture is powered by pluggable DSLs which drive key decisions:
| Phase | DSL Module Used |
|---|---|
| Fixed Role Invite | Role Invite Creator DSL |
| Post Role Creation | Post Role Creation DSL |
| Role Plan + Retrieval | Role Search Plan + Retrieve DSL |
| Application PQT Check | Initial PQT Checker DSL |
| Application Evaluation | Application Evaluation DSL |
| Role Removal Validation | Post Role Remover DSL |
| Role Auction Construction | Role Auction Creator DSL |
This extensibility allows organizations to customize behavior per role type or environment without code changes.
Integration Points
| External System | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Constraints DB | Stores initial constraint specs |
| Auction System | Manages auction lifecycle for contested roles |
| Human Intervention | Enables manual approvals or feedback loops |
| Messaging Backbone | Publishes updates and result messages |
| Org Association API | Adds new subjects to the organizational context |
Roles Schemas
This section describes the data structures used by the role system. Each schema is represented as a Python data class and stored as a MongoDB document. Below are the definitions and explanations for each schema.
SubjectRolesMapping
@dataclass
class SubjectRolesMapping:
subject_id: str = ''
role_ids: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
subject_type: str = ''
job_space_id: str = ''
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
subject_id |
str |
Unique identifier for the subject |
role_ids |
List[str] |
List of role IDs assigned to the subject |
subject_type |
str |
Type/category of the subject (e.g., human, agent, system) |
job_space_id |
str |
Identifier for the job space or context in which this mapping exists |
RoleGroupMapping
@dataclass
class RoleGroupMapping:
role_id: str = ''
role_type: str = ''
group_ids: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
job_space_id: str = ''
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
role_id |
str |
Unique ID for the role |
role_type |
str |
Type of role (used to refer to the assignment policy and configuration) |
group_ids |
List[str] |
List of group IDs associated with this role |
job_space_id |
str |
Context-specific ID used for logical separation |
RoleTypeAssignmentMapping
@dataclass
class RoleTypeAssignmentMapping:
role_type: str = ''
role_assignment_type: str = ''
role_post_removal_dsl_workflow_id: str = ''
role_post_addition_dsl_workflow_id: str = ''
position_filled: bool = False
job_space_id: str = ''
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
role_type |
str |
Unique name/identifier of the role type |
role_assignment_type |
str |
Can be "fixed", "dynamic_single_subject", or "dynamic_multi_subject" |
role_post_removal_dsl_workflow_id |
str |
DSL ID that is executed to determine if a subject can be removed from the role |
role_post_addition_dsl_workflow_id |
str |
DSL ID that is executed to validate a subject’s qualification before assigning the role |
position_filled |
bool |
Applicable to single-subject roles to prevent multiple concurrent assignments |
job_space_id |
str |
Context identifier for logical grouping or scoping |
GroupConstraintsMapping
@dataclass
class GroupConstraintsMapping:
group_id: str = ''
group_type: str = ''
constraint_ids: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
job_space_id: str = ''
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
group_id |
str |
Unique ID for the group |
group_type |
str |
Type or classification of the group |
constraint_ids |
List[str] |
List of constraint IDs associated with this group |
job_space_id |
str |
Context ID to scope constraints to a particular job environment |
RoleApplication
@dataclass
class RoleApplication:
role_application_id: str = ''
application_data: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
submission_time: int = 0
status: str = 'pending'
response_data: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
role_application_id |
str |
Unique ID generated per role application |
application_data |
dict |
Raw application payload submitted by the subject or automation |
submission_time |
int |
Timestamp (epoch-style integer) when the application was submitted |
status |
str |
Current status: "pending", "failed", or "success" |
response_data |
dict |
The result or reason for success/failure after processing the application |
API Documentation
Each of the following APIs allows you to interact with a specific MongoDB-backed data store that supports role-based assignments and subject mappings.
All APIs return responses in the following format:
{
"success": true,
"data": ...,
"error": null
}
If the operation fails:
{
"success": false,
"data": null,
"error": "Reason for failure"
}
1. SubjectRolesMapping APIs
POST /subject-roles
Query subject-role mappings based on a filter.
Request Body
{
"subject_type": "human"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/subject-roles \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"subject_type": "human"}'
GET /subject-roles/\
Get all roles mapped to a specific subject.
Example
curl http://localhost:8082/subject-roles/subject_123
2. RoleGroupMapping APIs
POST /role-group
Query role-group mappings by role type, group IDs, or job space.
Request Body
{
"role_type": "moderator"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/role-group \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"role_type": "moderator"}'
GET /role-group/\
Fetch group mapping for a specific role.
Example
curl http://localhost:8082/role-group/role_abc123
3. RoleTypeAssignmentMapping APIs
POST /role-type
Insert a new role type assignment configuration.
Request Body
{
"role_type": "admin",
"role_assignment_type": "dynamic_single_subject",
"role_post_removal_dsl_workflow_id": "dsl_removal_1",
"role_post_addition_dsl_workflow_id": "dsl_addition_1",
"position_filled": false,
"job_space_id": "space1"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/role-type \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @role_type.json
PUT /role-type/\
Update an existing role type entry.
Request Body
{
"position_filled": true
}
Example
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8082/role-type/admin \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"position_filled": true}'
DELETE /role-type/\
Delete a role type assignment entry.
Example
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8082/role-type/admin
POST /role-type
Query role type configurations.
Request Body
{
"role_assignment_type": "dynamic_single_subject"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/role-type \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"role_assignment_type": "dynamic_single_subject"}'
GET /role-type/\
Fetch a single role type entry by ID.
Example
curl http://localhost:8082/role-type/admin
4. GroupConstraintsMapping APIs
POST /group-constraints
Insert a new group constraints mapping.
Request Body
{
"group_id": "team_alpha",
"group_type": "security",
"constraint_ids": ["c1", "c2"],
"job_space_id": "space1"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/group-constraints \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @group_constraints.json
PUT /group-constraints/\
Update constraint IDs or other fields of a group.
Request Body
{
"constraint_ids": ["c3"]
}
Example
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8082/group-constraints/team_alpha \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"constraint_ids": ["c3"]}'
DELETE /group-constraints/\
Delete a group’s constraint mapping.
Example
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8082/group-constraints/team_alpha
POST /group-constraints
Query group constraints based on filters.
Request Body
{
"group_type": "security"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/group-constraints \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"group_type": "security"}'
GET /group-constraints/\
Get a specific group’s constraint mapping.
Example
curl http://localhost:8082/group-constraints/team_alpha
5. RoleApplication APIs
POST /role-applications
Query applications submitted for roles.
Request Body
{
"status": "pending"
}
Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8082/role-applications \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"status": "pending"}'
GET /role-applications/\
Get the complete role application by ID.
Example
curl http://localhost:8082/role-applications/4fc3f890-3e0b-4a8d-9c70-b0317feef812
Understood. Here's the cleaned-up and final version of the /submit-role-task documentation with no emojis, and all flow explanations and DSL tables properly included.
/submit-role-task API
Endpoint
POST /submit-role-task
This API queues a role application task for asynchronous execution. It supports multiple flows including direct assignment, criteria-based selection, auction-based selection, and role removal. The processing is performed in the background by the RolesExecutor class.
A unique role_application_id is generated and returned in the response. This ID can be used later to query the application status or result.
Request Schema
{
"action": "assign_direct | assign_by_criteria | assign_by_auction | remove",
...
}
The required fields depend on the value of the action.
Flow 1: Direct Assignment (assign_direct)
This flow allows manually assigning a specific subject to a role.
Request Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
action |
string | Yes | Must be "assign_direct" |
role_application_id |
string | Yes | Unique identifier for the application |
application_data |
dict | Yes | Role-related metadata or criteria |
subject_id |
string | Yes | ID of the subject to be assigned |
subject_data |
dict | Yes | Metadata about the subject |
Explanation
- The system verifies that the role type supports dynamic assignment.
- It runs a PQT DSL to determine if the subject is eligible.
- It then runs an evaluation DSL to verify qualifications.
- If both checks pass, the subject is associated with the role and the database is updated.
Flow 2: Criteria-Based Assignment (assign_by_criteria)
This flow selects a subject automatically based on a filter and selection DSL.
Request Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
action |
string | Yes | Must be "assign_by_criteria" |
role_application_id |
string | Yes | Unique identifier for the application |
application_data |
dict | Yes | Metadata for the role |
selection_criteria |
dict | Yes | Contains filtering rules and selection DSL |
Inside selection_criteria:
{
"filter_data": { ... },
"selection_dsl_workflow_id": "dsl_subject_selector"
}
Explanation
- This flow is used when no subject is specified and should be selected dynamically.
- The
SubjectsSearchclient applies the filter using the specified DSL to return a list of eligible subjects. - The first matching subject is chosen and passed through the evaluation DSL.
- If successful, the subject is assigned and recorded.
Flow 3: Auction-Based Assignment (assign_by_auction)
This flow accepts a list of potential subjects, runs an auction DSL, and assigns the role to the selected winner.
Request Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
action |
string | Yes | Must be "assign_by_auction" |
role_application_id |
string | Yes | Unique identifier for the application |
application_data |
dict | Yes | Role-related metadata |
subject_list |
list | Yes | List of subjects competing for the role |
Each subject entry:
{
"subject_id": "user_123",
"subject_data": {
"experience": 5,
"domain": "healthcare"
}
}
Explanation
- The system runs an auction creation DSL that evaluates all candidates and generates a payload.
- The auction payload is submitted to the
AuctionClient. - Once a winner is selected, that subject is passed through the evaluation DSL.
- If eligible, the subject is associated with the role and the system updates all relevant mappings.
Flow 4: Role Removal (remove)
This flow removes a subject from a role based on a DSL check.
Request Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
action |
string | Yes | Must be "remove" |
role_id |
string | Yes | ID of the role instance |
subject_id |
string | Yes | ID of the subject to be removed |
Explanation
- The system fetches the role type and ensures it's not a fixed role.
- It runs a removal DSL to verify whether the subject can be removed from this role.
- If approved, the role is removed from
RoleGroupMapping, and also from the subject’srole_idsarray inSubjectRolesMapping.
DSL Workflows Used
The system uses several DSL workflows defined per role type to handle eligibility, selection, and removal logic.
| DSL Field | Purpose |
|---|---|
role_initial_pqt_checker_dsl_id |
Preliminary qualification check before any role evaluation |
role_application_eval_dsl_id |
Full evaluation to confirm the subject is eligible for the role |
selection_dsl_workflow_id |
Used in criteria-based flow to select a subject |
role_auction_creation_dsl_workflow_id |
Used to generate auction payload from a list of subjects |
role_removal_check_dsl_workflow_id |
Used to determine if a subject can be removed from a role |
These DSL workflow IDs are stored in the RoleTypeAssignmentMapping collection.
Response
{
"success": true,
"role_application_id": "generated-uuid"
}
To check the processing status or final result:
curl http://localhost:8082/role-applications/<role_application_id>