Org Job contracts system
Introduction
The Job–Contract Mapping System is a backend service designed to facilitate the structured generation, management, and retrieval of contracts associated with computational jobs in automated AI workflows. It provides a consistent interface to define job specifications, execute domain-specific contract generation logic, and maintain persistent mappings between jobs and their resulting contracts.
This system acts as an intermediary layer between a job specification interface and the contracts infrastructure. It supports both RESTful and GraphQL query mechanisms, allowing users and internal services to programmatically retrieve and inspect how a given task is tied to a set of generated contracts.
A core feature of this system is the ability to interpret job specifications using an external DSL (domain-specific language) execution engine. The system can also integrate with a subject intervention mechanism to support human-in-the-loop contract shaping, enabling runtime validation, negotiation, or enrichment before finalizing contract submissions.
Key functionalities include:
- Executing DSL workflows to generate contract specifications.
- Submitting contract definitions to the Contracts System via HTTP APIs.
- Persistently mapping job identifiers (task and sub-task) to contract identifiers.
- Supporting flexible query patterns over stored mappings using REST and GraphQL.
This documentation describes the architecture, data models, and API specifications for integrating with and operating the Job–Contract Mapping System.
Architecture
The Job–Contract Mapping System is structured as a modular backend service that transforms job specifications into formal contracts through an automated and optionally human-assisted pipeline. It integrates with a DSL execution engine, a human intervention interface, and an external Contracts API, and it maintains persistent job-to-contract mappings in a MongoDB-backed datastore.
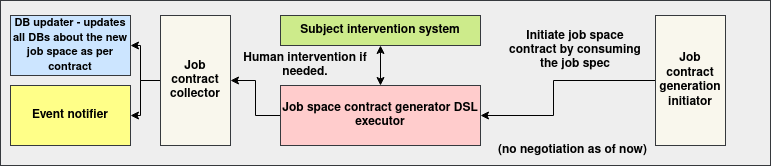
The system is composed of the following key components:
- Job Contract Initiator API: A RESTful entrypoint that accepts job specifications and orchestrates the contract generation flow.
- DSL Executor: Executes a domain-specific workflow to translate job input into contract artifacts.
- Subject Intervention System (optional): Provides a mechanism for human-in-the-loop editing or validation of job data prior to contract generation.
- Contracts API Client: Submits the generated contracts to the central Contracts System using HTTP APIs.
- Mapping Database: Persists the relationship between job identifiers and resulting contract IDs, supporting both REST and GraphQL-based query interfaces.
This architecture is designed to be extensible, policy-aware, and suitable for environments requiring traceable contract lifecycle management linked to computational task execution. It supports asynchronous feedback loops, structured validation, and metadata-first searchability, enabling tight integration with larger AI orchestration or governance frameworks.
Schema
The central data model in the Job–Contract Mapping System is the JobSpaceContractsMapping, which establishes a link between a computational job (identified by a task_id and optionally a sub_task_id) and one or more generated contracts. This mapping allows systems to track, query, and verify which contracts were derived from which job specifications.
JobSpaceContractsMapping Data Class
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from typing import List, Dict
@dataclass
class JobSpaceContractsMapping:
task_id: str
sub_task_id: str = ''
contract_ids: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
metadata: Dict = field(default_factory=dict)
@property
def key(self) -> str:
return f"{self.task_id}::{self.sub_task_id}" if self.sub_task_id else self.task_id
def to_dict(self) -> dict:
return {
"task_id": self.task_id,
"sub_task_id": self.sub_task_id,
"key": self.key,
"contract_ids": self.contract_ids,
"metadata": self.metadata,
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data: dict) -> 'JobSpaceContractsMapping':
return cls(
task_id=data.get("task_id", ""),
sub_task_id=data.get("sub_task_id", ""),
contract_ids=data.get("contract_ids", []),
metadata=data.get("metadata", {})
)
Field Definitions
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
task_id |
str |
Identifier of the primary job or task. This is typically unique per job instance. |
sub_task_id |
str |
Optional sub-task identifier to distinguish individual stages or phases of a job. |
contract_ids |
List[str] |
A list of unique identifiers for contracts that were generated for this job. |
metadata |
Dict |
Arbitrary key-value pairs associated with the job or contract context. |
key |
str (computed) |
A unique identifier for the mapping, composed as <task_id>::<sub_task_id> if sub_task_id is present, otherwise just task_id. Used as the MongoDB document _id. |
REST API
The REST API allows clients to create, update, retrieve, delete, and query job-to-contract mappings. It exposes endpoints to operate on mappings using keys, task identifiers, and arbitrary filters.
All responses are returned in JSON format. Each endpoint adheres to standard HTTP conventions and returns appropriate status codes.
Base URL
http://<host>:<port>/
Endpoints
1. Create a Mapping
POST /mappings
Creates a new job-to-contract mapping document.
- Request Body:
{
"task_id": "job-1",
"sub_task_id": "subtask-A",
"contract_ids": ["c1", "c2"],
"metadata": {"type": "inference"}
}
- Response:
{
"success": true,
"key": "job-1::subtask-A"
}
2. Get a Mapping by Key
GET /mappings/<key>
Retrieves a mapping document by its unique key.
-
Example:
/mappings/job-1::subtask-A -
Response:
{
"success": true,
"mapping": {
"task_id": "job-1",
"sub_task_id": "subtask-A",
"key": "job-1::subtask-A",
"contract_ids": ["c1", "c2"],
"metadata": {"type": "inference"}
}
}
3. Update a Mapping
PUT /mappings/<key>
Replaces an existing mapping with updated values.
-
Request Body: same as create
-
Response:
{
"success": true,
"mapping": { ... }
}
4. Delete a Mapping
DELETE /mappings/<key>
Deletes a mapping by its key.
- Response:
{
"success": true,
"message": "Deleted successfully"
}
5. List All Mappings
GET /mappings
Returns all job-to-contract mappings.
- Response:
{
"success": true,
"mappings": [ { ... }, { ... } ]
}
6. Get by Task ID
GET /mappings/by-task/<task_id>
Returns all mappings for a given task ID.
- Example:
/mappings/by-task/job-1
7. Get by Task and Sub-task
GET /mappings/by-task/<task_id>/<sub_task_id>
Returns a single mapping for a specific task and sub-task.
- Example:
/mappings/by-task/job-1/subtask-A
8. Query with Filter
POST /mappings/query
Queries mappings using a MongoDB-style JSON filter.
- Request Body:
{ "metadata.type": "inference" }
9. Raw Query (Unsafe, Internal Use)
POST /mappings/query/any
Accepts arbitrary Mongo-style queries for internal or admin tooling use.
GraphQL Interface
The GraphQL API provides a flexible, read-only query interface to the Job–Contract Mapping system. It exposes structured fields for retrieving mapping data using keys, task identifiers, or arbitrary filter criteria. The interface supports nested field selection and introspection via the built-in GraphiQL IDE.
This API is accessible via the following endpoint:
GET/POST /graphql
GraphiQL can be accessed through a browser for interactive query construction.
Supported Queries
1. Retrieve All Mappings
query {
allMappings {
taskId
subTaskId
key
contractIds
metadata
}
}
Returns all existing job-to-contract mappings.
2. Retrieve a Mapping by Key
query {
mappingByKey(key: "job-1::subtask-A") {
taskId
contractIds
metadata
}
}
Fetches a single mapping document using its unique key.
3. Retrieve Mappings by Task ID
query {
mappingsByTaskId(taskId: "job-1") {
key
contractIds
metadata
}
}
Returns all mappings for a given task ID.
4. Query with Arbitrary Filter (where)
query {
queryMappings(where: { metadata: { project: "alpha" } }) {
taskId
subTaskId
contractIds
metadata
}
}
Accepts a MongoDB-style where filter using JSON-compatible syntax and returns all matching mappings. This is the most flexible query mode and supports nested fields, $in, and other Mongo-style expressions.
Type: JobSpaceContractsMappingType
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
taskId |
String |
The task identifier |
subTaskId |
String |
Optional sub-task identifier |
key |
String |
Unique computed key (<task_id>::<sub_task_id>) |
contractIds |
[String] |
List of contract IDs mapped to this job |
metadata |
JSON |
Arbitrary metadata stored with the mapping |
Notes
- Only query operations are supported.
- No mutations or write capabilities are exposed via GraphQL.
- GraphQL filters (
where) mirror MongoDB-style filters but are JSON-safe and GraphQL-compliant. - The server uses
grapheneandGenericScalarto enable flexible JSON input.
Contract Generation Workflow
The contract generation workflow is responsible for transforming a structured job specification (JobSpec) into one or more formal contracts. This is accomplished through a multi-stage process that may optionally include human intervention, DSL-based transformation, contract validation, and persistent mapping.
This section describes the complete execution pipeline from job submission to contract registration.
Components Involved
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
JobSpec |
The input data structure describing the task, sub-task, participants, contract templates, constraints, and metadata. |
JobContractGenerationInitiator |
REST API entrypoint that accepts the JobSpec and invokes the DSL executor. |
JobSpaceContractGeneratorDSLExecutor |
Executes the contract logic defined by a DSL workflow using the configured workflow ID. |
SubjectInterventionSystem |
(Optional) Sends the spec for manual review via HTTP + NATS, then waits for user-modified input. |
ContractsDBClient |
REST client that sends each generated contract to the Contracts System's /contract endpoint. |
JobSpaceContractsMappingDB |
MongoDB-backed class that stores a mapping from job ID and sub-task ID to the resulting contract IDs. |
Execution Steps
1. Job Submission
A user or upstream system submits a JobSpec via POST /job/contract/generate.
2. Optional Human Review
If human_intervention_required is set to true, the spec is sent to a human reviewer. The system waits for feedback before proceeding.
3. DSL Execution
The configured DSL workflow (via workflow_id) is executed using new_dsl_workflow_executor(...). The output is expected to include a contract_spec dictionary containing one or more contract definitions.
4. Contract Submission
Each contract from the DSL output is submitted to the /contract REST API. The server validates and persists the contracts. Each response includes a generated contract_id.
5. Mapping Persistence
The system stores a JobSpaceContractsMapping document that records the job → contract(s) relationship. This includes task ID, sub-task ID, the list of generated contract_ids, and any metadata extracted from the contract.
6. Result Delivery
The final API response contains the mapping document, including all related contract IDs, in JSON format.