Org Constraints Executor – Introduction
Org Constraints Executor is a backend framework for registering, managing, and executing runtime constraints based on message types. These constraints are tied to specific DSL workflows and allow dynamic evaluation, validation, or transformation logic during organizational processing.
The system provides:
- A data model for representing and persisting constraint definitions
- A REST API for creating, updating, deleting, querying, and executing constraints
- A runtime executor (
ConstraintsManager) for loading and executing constraints in-memory
This system intentionally omits WebSocket support and is optimized for synchronous execution via REST.
Architecture
The Org Constraints Executor is a modular backend system designed to perform runtime validation of DSL-based organizational policies. It supports ad hoc constraint checks and queued asynchronous execution, and integrates seamlessly with role-based data stores and messaging systems.
This system ensures low-latency evaluation, role-aware logic execution, and parallelized constraint processing, using a layered architecture with hot caching, database access, queue-based execution, and DSL constraint runners.
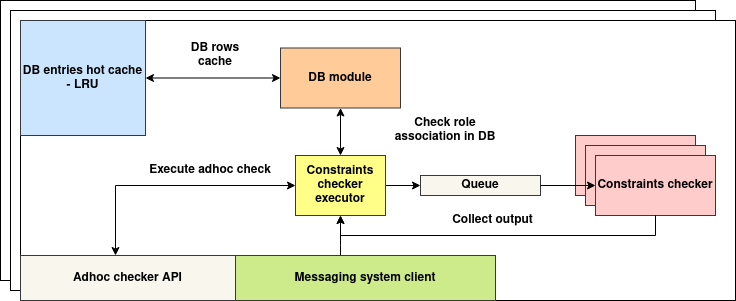
Core Architectural Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Adhoc Checker API | Public REST interface to trigger on-demand constraint execution by message type. Supports direct synchronous calls for fast evaluations. |
| Constraints Checker Executor | Core logic router that handles incoming constraint execution requests. It verifies role association, consults the DB module if necessary, and either executes inline or enqueues tasks. |
| DB Module | Interfaces with the backend database to resolve role associations and retrieve metadata needed for constraint execution. |
| DB Entries Hot Cache (LRU) | An in-memory Least-Recently-Used cache that stores frequently accessed DB rows. Reduces repetitive DB lookups for popular or recently validated subjects. |
| Queue | A lightweight in-memory or Redis-backed job queue that enables parallel constraint checks using worker threads or processes. |
| Constraints Checker | A set of worker instances that pull from the queue and execute the actual DSL logic associated with a constraint. Output is collected and returned to the executor. |
| Messaging System Client | Optional client integration that allows constraint results or side-channel notifications to be published over a message bus (e.g., Redis/NATS). Used for audit trails or reactive policies. |
Execution Flow
- An external caller invokes the Adhoc Checker API with a
message_typeand payload. -
The Constraints Checker Executor:
-
Checks the hot cache for role associations.
- Falls back to the DB Module if cache misses occur.
-
Once metadata is verified, the executor:
-
Executes the constraint immediately if lightweight,
- Or queues it for a Constraints Checker to process asynchronously.
-
The Constraints Checker:
-
Loads the DSL workflow associated with the message type.
- Executes the logic and returns the result.
- Results may optionally be published via the Messaging System Client.
This architecture ensures a balance between low-latency direct evaluation and scalable asynchronous execution, while preserving cache efficiency, constraint isolation, and modularity for plugging into broader policy enforcement systems.
Constraint Schema
OrgConstraints Data Class
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from typing import Dict, Any
@dataclass
class OrgConstraints:
message_type: str = ''
subject_id: str = ''
dsl_workflow_id: str = ''
constraint_metadata: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
message_type |
str |
Unique identifier for the type of message the constraint applies to |
subject_id |
str |
The user or entity this constraint is associated with |
dsl_workflow_id |
str |
DSL workflow ID that contains the constraint logic |
constraint_metadata |
Dict[str, Any] |
Optional metadata such as versioning or additional config |
REST API Endpoints
Create Constraint
Endpoint: POST /constraint
Description: Registers a new constraint with the system.
Request Body Example:
{
"message_type": "policy_check",
"subject_id": "user-001",
"dsl_workflow_id": "policy_workflow_v1",
"constraint_metadata": {
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/constraint \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @constraint.json
Get Constraint by Message Type
Endpoint: GET /constraint/<message_type>
Description: Retrieves a constraint configuration by its message type.
cURL:
curl http://localhost:8000/constraint/policy_check
Update Constraint
Endpoint: PUT /constraint/<message_type>
Description: Updates constraint metadata or properties.
Request Body Example:
{
"constraint_metadata": { "version": "1.1.0" }
}
cURL:
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8000/constraint/policy_check \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"constraint_metadata": {"version": "1.1.0"}}'
Delete Constraint
Endpoint: DELETE /constraint/<message_type>
Description: Deletes a constraint by its message type.
cURL:
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8000/constraint/policy_check
Query Constraints
Endpoint: POST /constraints
Description: Filters constraints using MongoDB-style query syntax.
Request Body Example:
{
"subject_id": "user-001"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/constraints \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"subject_id": "user-001"}'
Execute Constraint
Endpoint: POST /constraint/execute/<message_type>
Description: Executes the constraint logic and returns the output.
Request Body Example:
{
"subject_id": "user-001",
"dsl_workflow_id": "policy_workflow_v1",
"input_data": {
"policy": { "type": "ACCESS", "value": 5 }
}
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/constraint/execute/policy_check \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @execution.json
Get Constraint Metadata
Endpoint: GET /constraint/metadata/<message_type>
Description: Returns runtime metadata for a loaded constraint.
cURL:
curl http://localhost:8000/constraint/metadata/policy_check
Execution Lifecycle
- A constraint is registered via
POST /constraint. - On first execution, it is loaded into memory by the
ConstraintsManager. - Execution is handled by invoking the DSL workflow tied to the constraint.
- The result is returned synchronously via the REST API.
- The constraint stays cached in memory until explicitly unloaded or deleted.
Runtime Behavior
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
ConstraintsManager |
Central class for managing the lifecycle and execution of constraints |
ConstraintWrapper |
Internal wrapper that invokes DSL logic and exposes metadata |
| Auto-loading | Constraints are loaded into memory at first use |
| Caching | Constraints remain cached for reuse until explicitly cleaned |